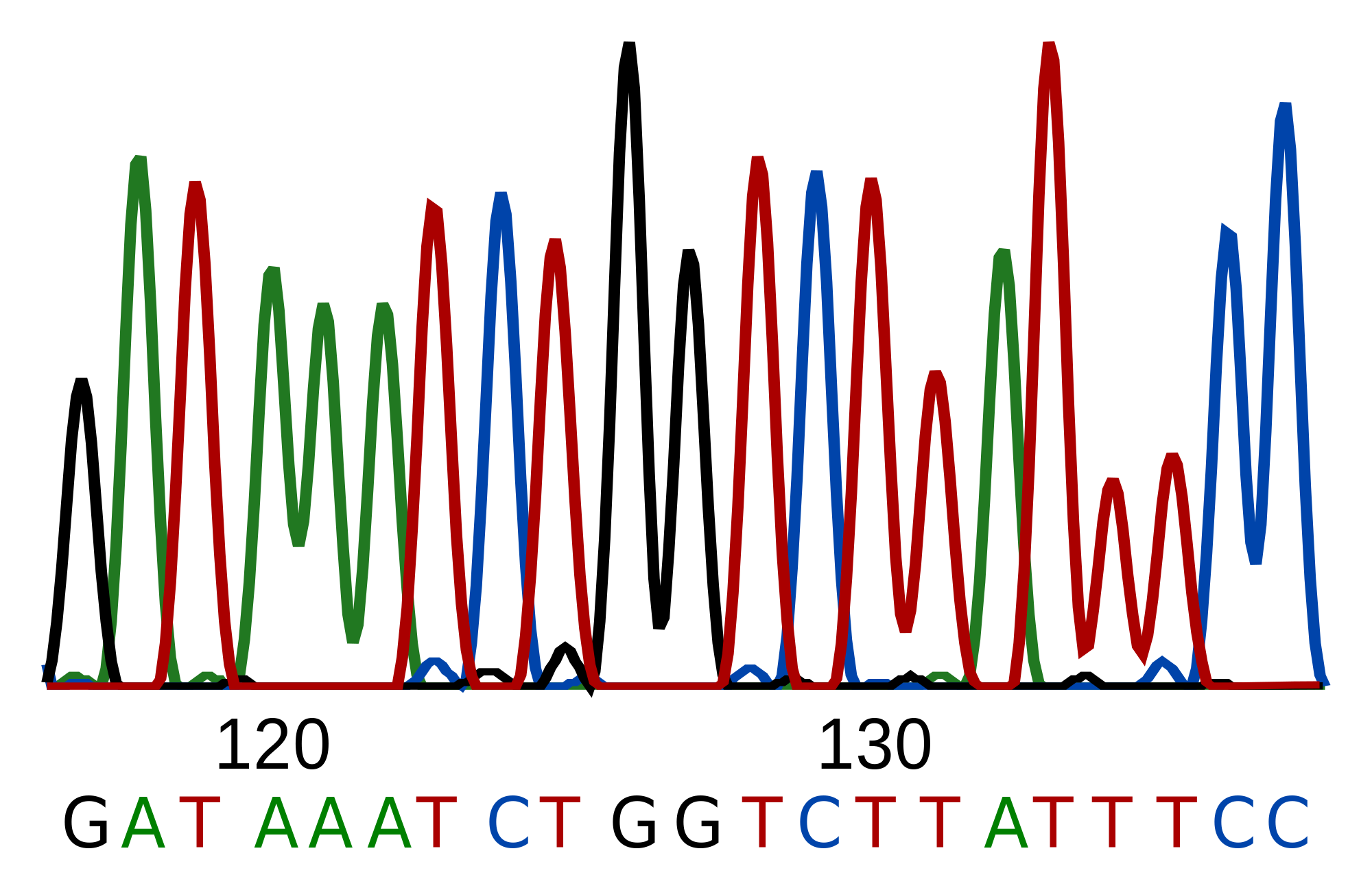
Sequence Data Meaning Biology . (i) biological samples/library preparation, (ii). In the vast realm of bioinformatics, sequence databases stand as repositories of. To explore complex biological questions, it is often necessary to access various data types from public. Scientific data must not be. an example is the relative abundance of biological sequence data in public databases such as genbank and.
from experiment.com
In the vast realm of bioinformatics, sequence databases stand as repositories of. Scientific data must not be. an example is the relative abundance of biological sequence data in public databases such as genbank and. (i) biological samples/library preparation, (ii). To explore complex biological questions, it is often necessary to access various data types from public.
What is DNA Sequencing and how does it work? Experiment
Sequence Data Meaning Biology To explore complex biological questions, it is often necessary to access various data types from public. an example is the relative abundance of biological sequence data in public databases such as genbank and. (i) biological samples/library preparation, (ii). In the vast realm of bioinformatics, sequence databases stand as repositories of. To explore complex biological questions, it is often necessary to access various data types from public. Scientific data must not be.
From www.uib.no
Bioinformatics Center for Data Science UiB Sequence Data Meaning Biology an example is the relative abundance of biological sequence data in public databases such as genbank and. Scientific data must not be. In the vast realm of bioinformatics, sequence databases stand as repositories of. (i) biological samples/library preparation, (ii). To explore complex biological questions, it is often necessary to access various data types from public. Sequence Data Meaning Biology.
From www.nsf.gov
Multimedia Gallery DNA Sequencing Process (Step 5) NSF National Sequence Data Meaning Biology an example is the relative abundance of biological sequence data in public databases such as genbank and. In the vast realm of bioinformatics, sequence databases stand as repositories of. To explore complex biological questions, it is often necessary to access various data types from public. Scientific data must not be. (i) biological samples/library preparation, (ii). Sequence Data Meaning Biology.
From www.mdpi.com
IJMS Free FullText Transcriptome Analysis Based on RNASeq in Sequence Data Meaning Biology Scientific data must not be. To explore complex biological questions, it is often necessary to access various data types from public. (i) biological samples/library preparation, (ii). an example is the relative abundance of biological sequence data in public databases such as genbank and. In the vast realm of bioinformatics, sequence databases stand as repositories of. Sequence Data Meaning Biology.
From experiment.com
What is DNA Sequencing and how does it work? Experiment Sequence Data Meaning Biology Scientific data must not be. In the vast realm of bioinformatics, sequence databases stand as repositories of. To explore complex biological questions, it is often necessary to access various data types from public. an example is the relative abundance of biological sequence data in public databases such as genbank and. (i) biological samples/library preparation, (ii). Sequence Data Meaning Biology.
From thednageek.com
DNA Basics Mutations The DNA Geek Sequence Data Meaning Biology Scientific data must not be. To explore complex biological questions, it is often necessary to access various data types from public. an example is the relative abundance of biological sequence data in public databases such as genbank and. (i) biological samples/library preparation, (ii). In the vast realm of bioinformatics, sequence databases stand as repositories of. Sequence Data Meaning Biology.
From www.mdpi.com
Biology Free FullText FLEXBAR—Flexible Barcode and Adapter Sequence Data Meaning Biology Scientific data must not be. In the vast realm of bioinformatics, sequence databases stand as repositories of. (i) biological samples/library preparation, (ii). an example is the relative abundance of biological sequence data in public databases such as genbank and. To explore complex biological questions, it is often necessary to access various data types from public. Sequence Data Meaning Biology.
From www.rna-seqblog.com
Biological validation of RNA sequencing data from formalinfixed Sequence Data Meaning Biology To explore complex biological questions, it is often necessary to access various data types from public. (i) biological samples/library preparation, (ii). In the vast realm of bioinformatics, sequence databases stand as repositories of. an example is the relative abundance of biological sequence data in public databases such as genbank and. Scientific data must not be. Sequence Data Meaning Biology.
From www.researchgate.net
The omics scheme. In this scheme, it has been shown that multiomics Sequence Data Meaning Biology In the vast realm of bioinformatics, sequence databases stand as repositories of. (i) biological samples/library preparation, (ii). Scientific data must not be. an example is the relative abundance of biological sequence data in public databases such as genbank and. To explore complex biological questions, it is often necessary to access various data types from public. Sequence Data Meaning Biology.
From www.myxxgirl.com
Flow Chart Showing Steps For Dna Sequence Analysis Esp My XXX Hot Girl Sequence Data Meaning Biology To explore complex biological questions, it is often necessary to access various data types from public. Scientific data must not be. an example is the relative abundance of biological sequence data in public databases such as genbank and. (i) biological samples/library preparation, (ii). In the vast realm of bioinformatics, sequence databases stand as repositories of. Sequence Data Meaning Biology.
From scitechdaily.com
Landmark Study Sequencing of 64 Full Human Genomes to Better Capture Sequence Data Meaning Biology To explore complex biological questions, it is often necessary to access various data types from public. (i) biological samples/library preparation, (ii). In the vast realm of bioinformatics, sequence databases stand as repositories of. an example is the relative abundance of biological sequence data in public databases such as genbank and. Scientific data must not be. Sequence Data Meaning Biology.
From dokumen.tips
(PPT) BIological database for protein sequence analysis DOKUMEN.TIPS Sequence Data Meaning Biology an example is the relative abundance of biological sequence data in public databases such as genbank and. In the vast realm of bioinformatics, sequence databases stand as repositories of. (i) biological samples/library preparation, (ii). Scientific data must not be. To explore complex biological questions, it is often necessary to access various data types from public. Sequence Data Meaning Biology.
From ce3c.ciencias.ulisboa.pt
Bioinformatics analysis of biological sequences — from sequence to Sequence Data Meaning Biology Scientific data must not be. an example is the relative abundance of biological sequence data in public databases such as genbank and. (i) biological samples/library preparation, (ii). In the vast realm of bioinformatics, sequence databases stand as repositories of. To explore complex biological questions, it is often necessary to access various data types from public. Sequence Data Meaning Biology.
From ukhsa.blog.gov.uk
What is Whole Genome Sequencing? UK Health Security Agency Sequence Data Meaning Biology (i) biological samples/library preparation, (ii). Scientific data must not be. To explore complex biological questions, it is often necessary to access various data types from public. In the vast realm of bioinformatics, sequence databases stand as repositories of. an example is the relative abundance of biological sequence data in public databases such as genbank and. Sequence Data Meaning Biology.
From www.thoughtco.com
Basics Introduction to Sequence Data Meaning Biology In the vast realm of bioinformatics, sequence databases stand as repositories of. (i) biological samples/library preparation, (ii). Scientific data must not be. an example is the relative abundance of biological sequence data in public databases such as genbank and. To explore complex biological questions, it is often necessary to access various data types from public. Sequence Data Meaning Biology.
From thebiologynotes.com
Nucleotide Databases Definition, Types, Examples, Uses Sequence Data Meaning Biology (i) biological samples/library preparation, (ii). To explore complex biological questions, it is often necessary to access various data types from public. Scientific data must not be. In the vast realm of bioinformatics, sequence databases stand as repositories of. an example is the relative abundance of biological sequence data in public databases such as genbank and. Sequence Data Meaning Biology.
From www.vedantu.com
What is a database in bioinformatics? Mention their two fundamental types. Sequence Data Meaning Biology an example is the relative abundance of biological sequence data in public databases such as genbank and. To explore complex biological questions, it is often necessary to access various data types from public. (i) biological samples/library preparation, (ii). Scientific data must not be. In the vast realm of bioinformatics, sequence databases stand as repositories of. Sequence Data Meaning Biology.
From br.pinterest.com
Circular Table Graphs Atomic Science, Science Biology, User Center Sequence Data Meaning Biology an example is the relative abundance of biological sequence data in public databases such as genbank and. In the vast realm of bioinformatics, sequence databases stand as repositories of. To explore complex biological questions, it is often necessary to access various data types from public. (i) biological samples/library preparation, (ii). Scientific data must not be. Sequence Data Meaning Biology.
From sciencerdmk.blogspot.com
Science Unit 5 blog The Human Genome Project and Gene Therapy Sequence Data Meaning Biology In the vast realm of bioinformatics, sequence databases stand as repositories of. (i) biological samples/library preparation, (ii). an example is the relative abundance of biological sequence data in public databases such as genbank and. To explore complex biological questions, it is often necessary to access various data types from public. Scientific data must not be. Sequence Data Meaning Biology.